A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock () or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
7 November 2016
adapted from the story by UNC-Chapel Hill Communications
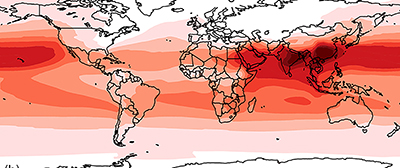
Where the world emits is more important than how much it emits, suggesting that the southward shift of emissions toward the equator is driving the increase in total ozone.
Since the 1980s, air pollution has increased worldwide, but it has increased at a much faster pace in regions close to the equator. Research from an international team led by a University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill scientist now reveals that this changing global emissions map is creating more total ozone worldwide compared to the amount of pollution being emitted, signaling an effect that could be difficult to reign in without strategic policy planning.
"Emissions are growing in places where there is a much greater effect on the formation of ozone," said Jason West, who led the research at UNC-Chapel Hill with former graduate student and first author Yuqiang Zhang. "A ton of emissions in a region close to the equator, where there is a lot of sunlight and intense heat, produces more ozone than a ton of emissions in a region farther from it."
The work published in Nature Geoscience provides a much-needed path forward on where in the world to strategically reduce emissions of pollutants that form ozone, which when present in the lower atmosphere, or troposphere, is one of the primary causes of air pollution-related respiratory problems and heart disease. (In the upper atmosphere, or stratosphere, ozone helps protect against the sun's ultraviolet rays.)
To drive home the point, West explained that China's emissions increased more than India's and Southeast Asia's from 1980 to 2010, but Southeast Asia and India, despite their lower growth in emissions during this period, appear to have contributed more to the total global ozone increase due to their proximity to the equator.
The reason is that ozone, a greenhouse gas and toxic air pollutant, is not emitted but forms when ultraviolet light hits nitrogen oxides (basically combustion exhaust from cars and other sources). When these pollutants interact with more intense sunlight and higher temperatures, the interplay speeds up the chemical reactions that form ozone. Higher temperatures near the equator also increase the vertical motion of air, transporting ozone-forming chemicals higher in the troposphere, where they can live longer and form more ozone.
"The findings were surprising," said West. "We thought that location was going to be important, but we didn't suspect it would be the most important factor contributing to total ozone levels worldwide. Our findings suggest that where the world emits is more important than how much it emits."
Zhang, West and colleagues, including CIRES researchers at CSD Owen Cooper and Audrey Gaudel, used a computer model to simulate the total amount of ozone in the troposphere, the part of the atmosphere where ozone is harmful to humans and agriculture, between 1980 and 2010. Since emissions have shifted south during this period, they wanted to answer, what contributed more to the increased production of ozone worldwide: the changing magnitude of emissions or location?
To find out, the team used a unique European data set of ozone observations from commercial aircraft to confirm the strong increases in ozone above Asia. Then they superimposed a map of how much pollution the world was emitting in 1980 onto where the world was emitting it in 2010, and vice versa, in addition to another scenario of the growth of methane gas, to determine what is driving the world's increase in ozone production.
"Location, by far," said West, associate professor of environmental sciences in the UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health.
The findings point to several strategies for reducing ground-level ozone across the world, such as decreasing emissions of ozone precursors in regions close to the equator, particularly those with the fastest growth of emissions. However, concerns exist for policy makers.
"A more challenging scenario is that even if there is a net reduction in global emissions, ozone levels may not decrease if emissions continue to shift toward the equator," said Cooper. "But continuing aircraft and satellite observations of ozone across the tropics can monitor the situation and model forecasts can guide decision making for controlling global ozone pollution."
Yuqiang Zhang, Owen R. Cooper, Audrey Gaudel, Anne M. Thompson, Philippe Nédélec, Shin-Ya Ogino, and J. Jason West, Tropospheric ozone change from 1980 to 2010 dominated by equatorward redistribution of emissions, Nature Geoscience, doi:10.1038/ngeo2827, 2016.
Ozone is an important air pollutant at the surface, and the third most important anthropogenic greenhouse gas in the troposphere. Since 1980, anthropogenic emissions of ozone precursors—methane, non-methane volatile organic compounds, carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides (NOx)—have shifted from developed to developing regions. Emissions have thereby been redistributed equatorwards, where they are expected to have a stronger effect on the tropospheric ozone burden due to greater convection, reaction rates and NOx sensitivity. Here we use a global chemical transport model to simulate changes in tropospheric ozone concentrations from 1980 to 2010, and to separate the influences of changes in the spatial distribution of global anthropogenic emissions of short-lived pollutants, the magnitude of these emissions, and the global atmospheric methane concentration. We estimate that the increase in ozone burden due to the spatial distribution change slightly exceeds the combined influences of the increased emission magnitude and global methane. Emission increases in Southeast, East and South Asia may be most important for the ozone change, supported by an analysis of statistically significant increases in observed ozone above these regions. The spatial distribution of emissions dominates global tropospheric ozone, suggesting that the future ozone burden will be determined mainly by emissions from low latitudes.