A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock () or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
AGES+ (AEROMMA+CUPiDS, GOTHAAM, EPCAPE, STAQS and others) encompasses all the different field activities during the summer of 2023.
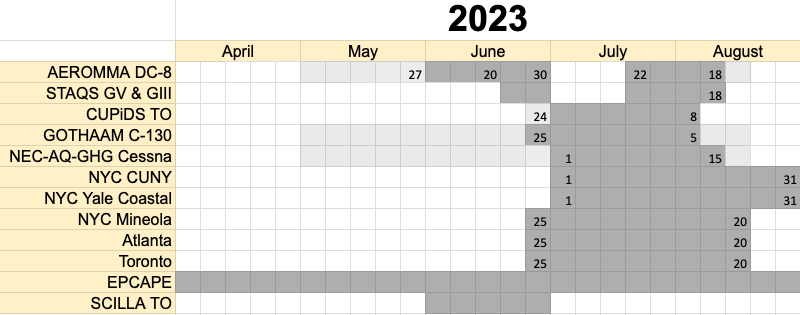
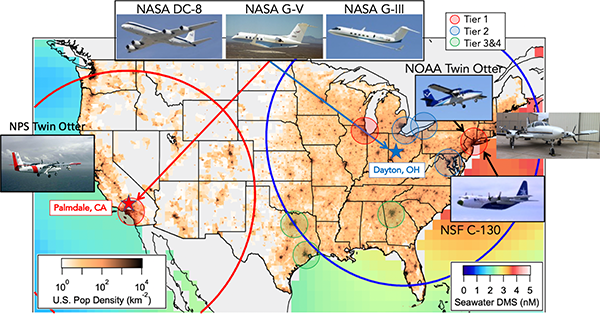
NOAA sponsored field mission planned for Summer 2023 will address emerging research needs in urban air quality, marine emissions, climate feedbacks, and atmospheric interactions at the marine-urban interface and future satellite capabilities of monitoring atmospheric composition over North America. Data will be collected from the NASA DC-8 research aircraft.
NOAA will deploy the NOAA Twin Otter research aircraft to the New York City region in the summer of 2023 to support the overall AEROMMA science objectives related to urban emissions as affected by coastal meteorology. Data will be used to study diurnal forcing of atmospheric dynamics on urban plume transport and mixing in coastal regions.
NASA's Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of POllution (TEMPO) mission launches early 2023 to provide geostationary observations of air quality over North America. With this addition of high-resolution satellite measurements, the STAQS mission seeks to integrate TEMPO satellite observations with traditional air quality monitoring to improve understanding of air quality science and increase societal benefit. Researchers will target two primary domains in Los Angeles and New York City and several secondary domains across North America with ground and airborne based measurements from the NASA GV research aircraft.
The National Science Foundation (NSF) / National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) sponsored field mission rescheduled for Summer 2025 will focus on the biogeochemical interactions in urban, rural, and marine regions. Data will be collected from the NCAR/NSF C-130 research aircraft.
The NOAA Air Resources Lab (ARL) and University of Maryland (UMD) will deploy a fully instrumented Cessna 402 research aircraft in the northeast corridor region of the U.S. from Washington, DC to New York City in the summer of 2023. Data will be used to characterize the meteorology and chemistry leading to air pollution events and emissions of greenhouse gases over this region, and provide the scientific basis for effective air quality and climate policies.
The Naval Postgraduate School (NPS, formerly CIRPAS) Twin Otter research aircraft will deploy to San Diego in June 2023, the month of climatological maximum low cloud cover. Flights will compliment the Eastern Pacific Cloud Aerosol Precipitation Experiment (EPCAPE).
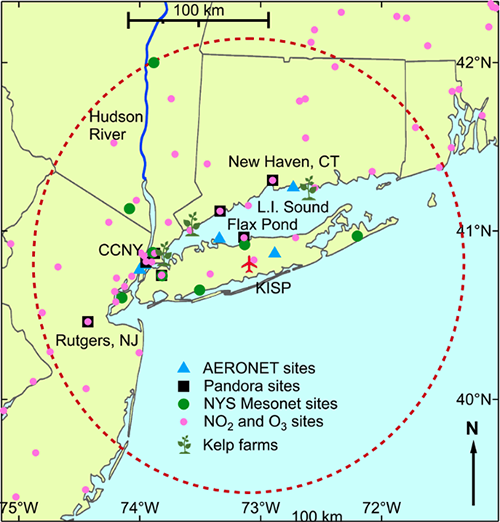
Researchers from Yale University, Aerodyne Research Inc., and other AC4-funded collaborators plan to study emissions and oxidative aging of non-traditional gas-phase organic compounds in the greater New York City metropolitan area. Intensive measurements will be conducted during summer 2023, to coordinate with AEROMMA flights, from an elevated ground site at the The City University of New York (NYC CUNY) and a downwind ground site in Guilford, CT (NYC Yale Coastal Site).
Furthering NY-METS, FROG-NY applies the eddy covariance (EC) technique to derive a better understanding of urban emissions and deposition of volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds. Specifically, researchers from Colorado State Univeristy and the University of Minnesota will apply two complimentary time-of-flight chemical ionization mass spectrometry (ToF-CIMS) instruments to directly quantify the fluxes, vertical gradients, and concentrations of an expansive suite of reactive VOCs from an existing 62-meter tower in metropolitan NY (NYC Mineola).
NOAA will also deploy two ground-based NOAA lidars to Guilford, CT (NYC Yale Coastal Site) for the Coastal Urban Plume Dynamics Study (CUPiDS) in the summer of 2023 to support key AEROMMA science objectives related to urban emissions as affected by coastal meteorology.
Air (Ine)quality in New York City is a pilot project to map surface ozone and PM2.5 in underserved boroughs in New York City during heat wave events and to engage with their communities in Summer 2023. Researchers conduct the study to demonstrate the connection between detailed ground level observations, where pollution directly impacts human health, and the broader aircraft and satellite observations deployed under AEROMMA.
Atlanta is a hot-spot of both ozone and secondary organic aerosol (SOA), and much of the summer is typically classified as "moderate" according to the air quality index. The city is subject to high anthropogenic and biogenic emissions along with increasingly severe heat waves. Atlanta has been the location of several previous studies investigating biogenic/anthropogenic interactions. Researchers from Georgia Tech will make ground-based observations overlapping AEROMMA science flights, allowing us to build on and update previous work with new chemical detail.
Severe ozone in counties adjacent to the Great Lakes shorelines, particularly Lake Michigan, is a longstanding air quality challenge. The lake breeze is present during a majority of the days with high ozone, with steep ozone gradients along the lakeshore and concentration of pollutants in a shallow layer. Ground site assets are in place overlapping CUPiDS science flights to study complex interactions between lake boundary layers, lake breezes and urban emissions.
Toronto is the largest Canadian city included in AEROMMA, with a metropolitan population exceeding seven million and regional population approaching ten million. Although precursors to ground-level ozone have been reduced in Toronto over past decades, exceedances of the 8-hour ozone Canadian Ambient Air Quality Standard are still common. Researchers from York University will make ground-based observations at a site located in an urban/suburban transition zone that is not impacted by any large local sources (i.e., >500 m from any major roads). At 20 km north of downtown Toronto and Lake Ontario, the site is ~2-3 hours transport time from major sources in downtown Toronto and is typically not impacted by lake breeze fronts until late in the afternoon during summer.
The Department of Energy ARM (Atmospheric Radiation Measurement) experiment planned for 2022-2023 focuses to characterize the extent, radiative properties, aerosol interactions, and precipitation characteristics of stratocumulus clouds in the Eastern Pacific across all four seasons at a coastal location, such as the Scripps Pier and the Scripps Mt. Soledad sites in La Jolla, California.